
- HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA HOW TO
- HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA FULL
- HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA SOFTWARE
- HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA PASSWORD
- HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA LICENSE
You’ll see examples of commands that will help you install different software, configs, and updates through Homebrew. In Terminal, run brew help to get started. If you don’t want your data to be collected and shared with the Homebrew developers, here’s the command you should run in Terminal to turn off analytics: brew analytics off Step 4: Set up Homebrew Here’s what’s typically collected: Homebrew User Agent, Google Analytics version, Homebrew analytics tracking ID, Homebrew analytics user ID, and data about the status of Google Analytics anonymous IP setting. This is not an obligatory step, but we’d better warn you that Homebrew can share some of your data with developers since the tool is free and open-source. Wait a few minutes until you see the “Installation successful” message in Terminal.
HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA PASSWORD
Type your admin password (note that you won’t see your keystrokes in the Terminal window - it’s a security measure) > hit Return Open Terminal and type the following command:
HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA LICENSE
HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA HOW TO
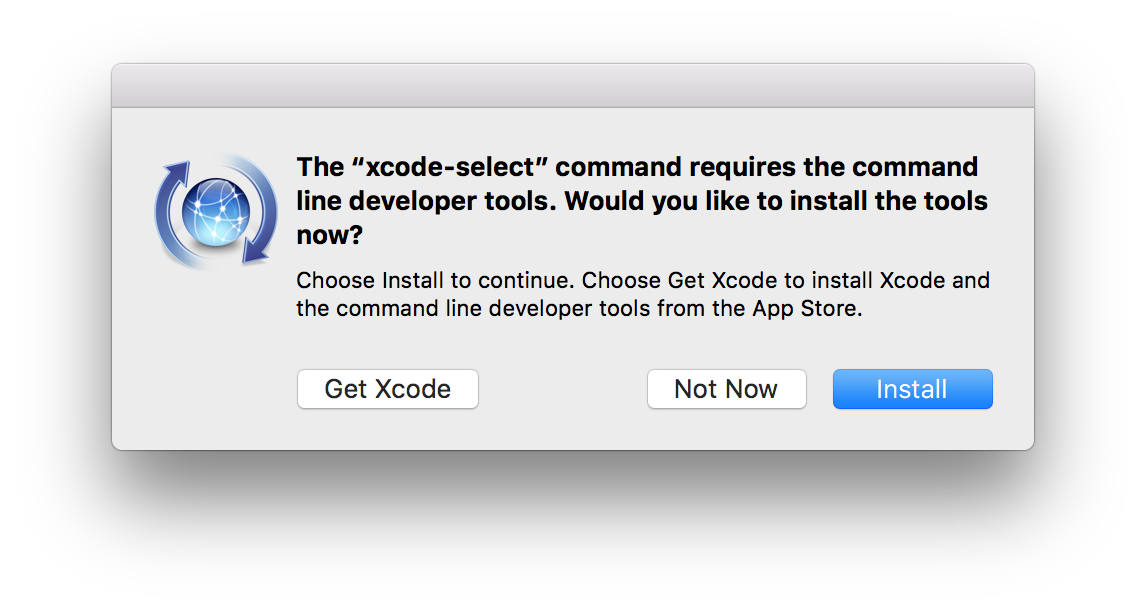
Here’s how to install command line tools for Xcode: To install some of the Homebrew package components, you need to install Xcode’s command line tools first (in case you haven’t done it before).
HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA SOFTWARE
Xcode is Apple’s native IDE, an integrated development environment that has all the tools you need for software development on Mac. Step 1: Install command line tools for Xcode Since some people don’t want to use curl for security reasons, there are ways to manually download and execute the script (but we won’t go into that here). The same applies to the process of uninstalling Homebrew. This method is the easiest and it’s recommended by the Homebrew team. Moving to the main part - ”install Homebrew Mac” - we should explain that the installation method we describe uses curl to download the installation script.
HOW TO INSTALL GIT FOR MAC OSX SIERRA FULL
The beauty of Setapp is that you don’t have to know the names of these apps or their full functionality - you just type your task in search (for example, “edit PDF”), and Setapp gives you the apps that can edit PDF. There are some simple default brew commands for installing single-file utilities, and more advanced subcommands called casks - you’ll have to use those to install multi-directory utilities. The main thing you should know as a user is that Homebrew acts through Terminal commands - you can install, update, and uninstall packages by typing a few words. To go easy on the coding jargon, we won’t be explaining how Homebrew works under the hood.
We also suggest a few tools similar to Homebrew you could benefit from. In this tutorial, we describe how to safely install and uninstall Homebrew on Mac. Package managers like Homebrew make the command line interface even more powerful. It helps streamline a lot of work, especially for software developers. By using the command line, you can solve many tasks on Mac by running commands in Terminal. The macOS command line interface can be intimidating - but there’s lots of value inside. Git is an essential tool for collaborating with other programmers.Unlock the power of top dev apps on Setapp. On the Select Components screen you’ll probably want to check on the option to have it put an additional icon On the Desktop, but otherwise, just keep clicking Next to go through the installer. The default options should be fine for most people. Proceed with the download/install process until it’s done. If you do not have it installed, you’ll be prompted to download and install the Xcode developer tools (which include Git). If it tells you a git version number, you already have Git installed. In the Terminal window, type the following and press Return: git -version

Go to Applications > Utilities and open Terminal.app.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
